Specialities
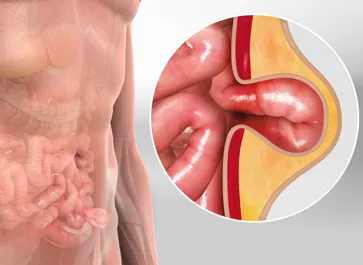
Surgical repair is the primary approach to address hernias, strengthening weakened tissues to prevent protrusion.
Bariatric surgery offers effective weight loss solutions for individuals struggling with obesity, improving overall health.
Laparoscopic surgery utilizes small incisions and specialized tools for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery time.
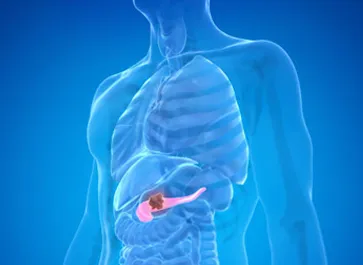
Pancreatic surgery is performed to treat conditions of the pancreas, often addressing tumors or chronic diseases.
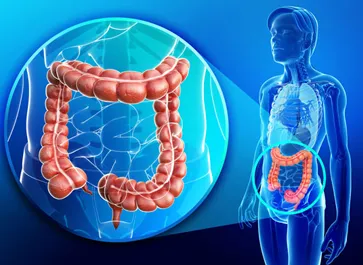
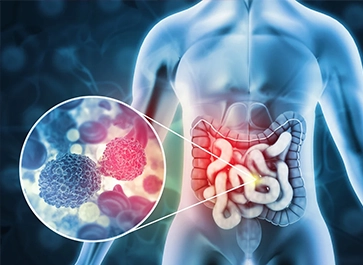
Colorectal surgery is used to treat diseases of the colon and rectum, such as cancer and inflammatory conditions.
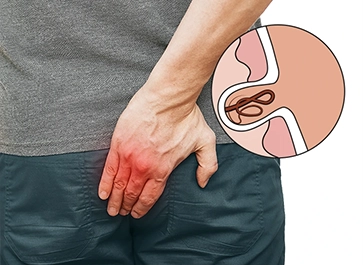
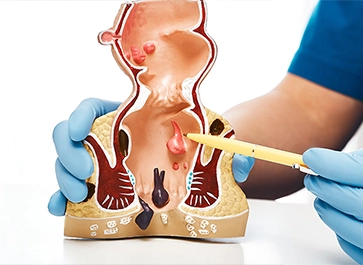
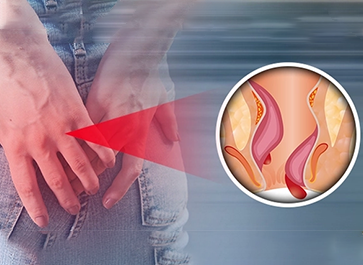
Piles treatment involves various medical and lifestyle interventions to alleviate the discomfort and symptoms associated with hemorrhoids, a common rectal condition.
Pilonidal sinus treatment involves surgical procedures to remove and repair the sinus tract that often forms near the tailbone, addressing a painful and recurrent condition.
Fissure treatment involves medical or surgical interventions to heal or manage painful tears or cracks in various body tissues, such as anal fissures or skin fissures.
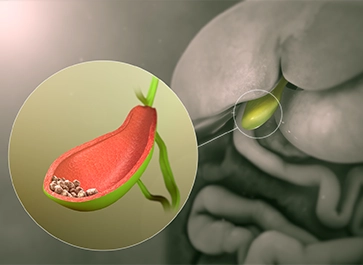
Gallbladder stone treatment involves various medical and surgical approaches to alleviate symptoms and remove gallstones, such as cholecystectomy or non-invasive techniques like shock wave lithotripsy.
Fistula treatment is a medical procedure aimed at repairing abnormal connections or passages between organs or tissues in the body, typically involving surgery to close or redirect these channels.
Colorectal cancer treatment encompasses a range of medical interventions, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapies, tailored to combat cancerous growths in the colon or rectum.