Specialities
- Home
- Pilonidal sinus Treatment
- Home
- Pilonidal sinus Treatment
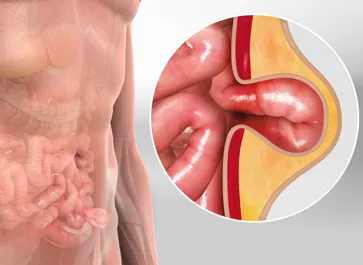
What is Pilonidal sinus
A pilonidal sinus, also known as a pilonidal cyst or sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease, is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the region just above the cleft of the buttocks, near the tailbone (coccyx). This condition is characterized by the development of a small tunnel or channel under the skin that can become infected, causing pain and discomfort.
What are the Causes of Pilonidal sinus?
- Hair and Hair Follicles:Loose or ingrown hairs can penetrate the skin in the natal cleft (the groove or crease between the buttocks). When hair punctures the skin, it can lead to irritation and inflammation, which, over time, can contribute to the formation of a pilonidal sinus.
- Friction and Pressure:Continuous friction and pressure in the intergluteal area, such as those caused by sitting for extended periods or by tight clothing, can exacerbate the irritation and encourage the development of a sinus tract.
- Anatomical Factors:The shape of the natal cleft can influence the likelihood of pilonidal sinus formation. A deep, clefted area may be more prone to trapping hair and promoting irritation.
- Sweat and Bacteria:The combination of sweat and bacteria in the intergluteal area can contribute to infection and the formation of an abscess within the pilonidal sinus.
- Genetic Factors:Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing pilonidal sinuses. A family history of the condition can be a contributing factor.
- Obesity:Excess body weight and obesity can increase the risk of pilonidal sinus, as it can lead to more skin folds and moisture, which can exacerbate the factors mentioned above.
What are the Symptoms of Pilonidal sinus?
The symptoms of pilonidal sinus, also known as pilonidal cyst or sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease, can vary in severity, and not everyone with the condition experiences symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they often include the following:
- Pain and Tenderness: Pain in the intergluteal area, typically near the tailbone (coccyx), is a common symptom of pilonidal sinus. The pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, especially during activities such as sitting or walking.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected area may become swollen, and the skin can appear red and inflamed.
- Abscess Formation: In some cases, the sinus tract becomes infected, leading to the development of an abscess. An abscess is a painful, swollen lump filled with pus. It may be accompanied by an increase in pain and tenderness.
- Pus and Drainage:Pilonidal sinuses often drain pus, blood, or other fluids, particularly when they become infected. You may notice drainage from small openings or pits in the skin near the cleft of the buttocks.
- Fever and Chills:An infection of a pilonidal sinus can lead to symptoms of illness, including fever, chills, and a general feeling of being unwell.
- Foul Odor:The drainage from a pilonidal sinus can have a foul odor due to the presence of pus and bacteria.
- Recurrent Symptoms: Pilonidal sinuses can be recurrent, with symptoms coming and going over time. Some individuals may experience repeated episodes of pain, abscess formation, and drainage.
- Itching and Discomfort: The area may itch, and there may be a general sense of discomfort, particularly when sitting for extended periods.
It's important to note that not everyone with a pilonidal sinus experiences symptoms, and some individuals may have asymptomatic (without symptoms) sinus tracts. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary from person to person. If you suspect you have a pilonidal sinus or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it's advisable to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment. Infected pilonidal sinuses may require medical attention and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Diagnosis for Pilonidal sinus
The diagnosis of pilonidal sinus (pilonidal cyst or sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease) typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and, in some cases, imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the condition. Here's an overview of the diagnostic process:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history, asking about your symptoms, when they first appeared, and whether you have a history of pilonidal sinus or similar issues. A physical examination of the affected area is conducted to assess the presence of a sinus or abscess, tenderness, redness, and drainage.
- Clinical Evaluation:During the physical examination, your healthcare provider will closely inspect the intergluteal or natal cleft, looking for signs of sinus openings or abscesses. They may gently palpate the area to assess tenderness and drainage.
- Imaging Studies:In some cases, imaging studies may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the extent of the condition. Common imaging options include:
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound can help visualize the sinus tracts and abscesses and determine their depth and structure.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides detailed images of the pilonidal sinus and surrounding tissues, which can aid in planning treatment, especially when the condition is complex.
- Abscess Aspiration: In some cases, your healthcare provider may perform an aspiration, which involves using a needle and syringe to draw out fluid or pus from an abscess. This can help confirm infection and guide treatment.
- Biopsy: Although not commonly required, a tissue biopsy may be recommended if there are concerns about other skin conditions or malignancies. A small tissue sample may be collected and examined under a microscope.
Treatments for Pilonidal sinus
The treatment of pilonidal sinus (pilonidal cyst or sacrococcygeal pilonidal disease) depends on the severity of the condition and whether it is complicated by infection or abscess formation.
Surgical Procedures:
Simple Incision and Drainage:
In some cases, particularly when an abscess is present, a simple incision and drainage procedure may be performed. This involves making an incision to release pus and fluid from the abscess. While this procedure provides immediate relief, it may not be curative, and recurrence can occur.
Surgical Excision:
Surgical excision is a common and effective treatment for pilonidal sinus. The procedure involves the complete removal of the sinus tracts and any surrounding tissue. There are two main approaches to surgical excision:
Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation (DGHAL):
In some cases, particularly when an abscess is present, a simple incision and drainage procedure may be performed. This involves making an incision to release pus and fluid from the abscess. While this procedure provides immediate relief, it may not be curative, and recurrence can occur.
- Primary Closure: In this approach, the wound created by the excision is closed with sutures (stitches). This method is suitable for smaller, less complex pilonidal sinuses. The primary closure allows for faster wound healing.
- Open Healing (Secondary Closure):In cases of complex or infected pilonidal sinuses, the wound is left open after excision. It is allowed to heal naturally from the inside out. While this method has a longer healing time, it may reduce the risk of recurrence.
Flap Procedures:
Flap procedures are typically considered for complex or recurrent pilonidal sinuses. These procedures involve using tissue flaps to cover the wound after sinus excision. Flap surgeries aim to promote quicker and more effective healing while minimizing the risk of recurrence.
Laser Surgery:
Laser surgery, such as the use of a CO2 laser, is an alternative approach to traditional surgical excision. The laser is used to remove the sinus tracts and affected tissue while sealing blood vessels and minimizing bleeding. It is associated with less postoperative pain and quicker recovery in some cases.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a Pilonidal sinus?
A pilonidal sinus is a chronic skin condition characterized by the development of a small tunnel or channel under the skin, typically in the intergluteal area, near the tailbone (coccyx). It can become infected and cause pain and discomfort.
2. What are the common symptoms of Pilonidal sinus?
Common symptoms include pain, tenderness, swelling, redness, and the drainage of pus, blood, or other fluids from the affected area. Recurrent episodes of symptoms are also possible.
3. What causes Pilonidal sinus?
The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from the penetration of loose or ingrown hairs into the skin, leading to irritation and the formation of the sinus. Other factors like anatomical features and lifestyle may contribute.
4. Is surgery the only treatment for pilonidal sinus?
Surgery is often recommended for more severe or recurrent cases of pilonidal sinus. In milder cases, conservative management and lifestyle changes may be sufficient to manage symptoms and prevent recurrence.
5. What can I do to prevent pilonidal sinus?
Preventive measures include maintaining good personal hygiene in the intergluteal area, keeping the area dry, avoiding prolonged sitting, and hair removal or shaving in the affected area, especially if you have a lot of body hair.
6. Can pilonidal sinus come back after treatment?
Yes, pilonidal sinus can recur, especially if preventive measures are not followed or if the underlying factors contributing to the condition are not addressed. Recurrence is more likely in cases of incomplete or inadequate surgical removal.
7. How long does the recovery process take after surgery for pilonidal sinus?
Recovery time varies depending on the surgical approach used and individual factors. Healing after primary closure surgery may take a few weeks, while open healing (secondary closure) can take several months.
8. Can pilonidal sinus be treated with antibiotics alone?
While antibiotics can be used to treat infections associated with pilonidal sinus, they are not typically curative on their own. Surgical intervention is often needed to fully address the condition.
9. Is pilonidal sinus a hereditary condition?
While there is a genetic component to some cases, pilonidal sinus is not solely hereditary. A family history of the condition may indicate a genetic predisposition, but other factors like hair penetration and lifestyle play a role.
10. Can pilonidal sinus be a recurring problem throughout life?
Yes, pilonidal sinus can be a recurring issue for some individuals. Proper management, lifestyle changes, and adherence to preventive measures are essential to reduce the risk of recurrence.